Laparoscopic Surgery
What Is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy (pronounced "lap-a-ROSS-coe-pee") is a surgical procedure performed through very small incisions in the abdomen, using specialized instruments. A pencil-thin instrument called a laparoscope is used, and it gives the surgeon a view on a TV monitor, of the inside of the abdominal cavity.
A laparoscope has lenses like a telescope to magnify body structures, a powerful light to illuminate them, and a miniature video camera. The camera sends images of the inside of the body to a TV monitor in the operating room. Specialized surgical instruments can be inserted through the laparoscope, and through small incisions nearby.
This type of surgery is called 'minimally invasive' because of the very small incisions used. Yet major procedures can now be performed using this technique. The term laparoscopy is used when this type of surgery is performed in the abdomen. "Laparo" comes from a Greek word meaning "flank," which is the side of the body between the ribs and hips. Doctors use this term to refer to the abdomen. The term "scope" means to look at or examine. Many procedures once done through a large opening in the abdomen can now be done with the small incisions of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy has become the preferred surgical technique for some conditions, such as gallbladder disease.
What are the uses of Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy can be used either to diagnose or to treat various conditions. Or it may be used to identify a problem and treat it in the same operation.
Diagnostic laparoscopy allows the doctor to look at structures inside the abdomen and see whether they appear normal or abnormal. It becomes valuable when physical examinations, lab tests, x-rays, and computerized scans don't show exactly what is wrong and a diagnosis requires a direct look inside the body.
- It can be used to diagnose the cause of abdominal pain, pelvic pain, infertility, and other problems in abdominal organs.
- During a diagnostic laparoscopy, the doctor also can use tiny scissors and other instruments to snip a sample of tissue and take a biopsy. The tissue can be examined with a microscope to see if it is normal.
- Laparoscopy can be used to determine the stage of certain kinds of cancer. Stage means how far the cancer has advanced.
- Hospital emergency departments may use laparoscopy to decide on the treatment of patients with trauma, or accidental injury. The procedure can "see" internal bleeding or other problems that might not be detected otherwise.
Operative laparoscopy allows the doctor to treat a disease or condition. It usually involves removing diseased tissue or repairing damage to a structure in the abdomen. Laparoscopy also is used in assisted reproductive procedures for women who are infertile or having difficulty becoming pregnant.
Laparoscopic surgery also is called:
- Minimally invasive surgery, because the operation is done through the smallest possible incisions.
- Belly button surgery, because the laparoscope used for abdominal surgery is often inserted through a small incision near the belly button (umbilicus or navel).
- Band-Aid surgery, because the incisions for laparoscopy are so small that they can be covered with adhesive bandage strips.
- Endoscopic surgery, because the instrument used for minimally invasive procedures on parts of the body other than the abdomen is called an endoscope.
What Kinds Of Surgery Can Be Performed With Minimally Invasive Methods?
Dozens of different kinds of operations are now being done using these new minimally invasive techniques. These include operations on the abdomen, heart, reproductive organs, nerves, ear, nose, sinuses, throat, joints, chest organs, urinary tract, and blood vessels. These techniques are also used in plastic and reconstructive surgery.
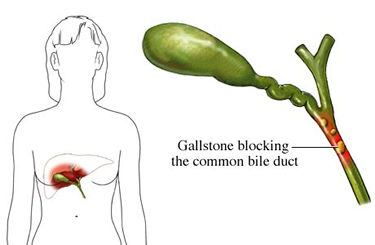
What Are The Advantages Of Laparoscopy?
- removal of a damaged or diseased spleen;
- inguinal hernia repairs, when part of the intestine bulges through a weakened segment of the abdominal wall;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- some problems of the colon (large intestine) or rectum; and
- removal of an infected or inflamed appendix.
Laparoscopy is easier on the patient because it uses a few very small incisions. For example, traditional "open surgery" on the abdomen usually requires a four- to five-inch incision through layers of skin and muscle. In laparoscopic surgery, the doctor usually makes two to three incisions that are about a half-inch long.