Emergency Stroke Management
Emergency Stroke Management
Definition
A stroke, sometimes known as a brain attack, happens when something blocks blood supply to a part of the brain or when a blood vessel in the brain bursts. In both case, parts of the brain come to be damaged or die. A stroke can reason lasting brain damage, long-time period disability, or maybe death.
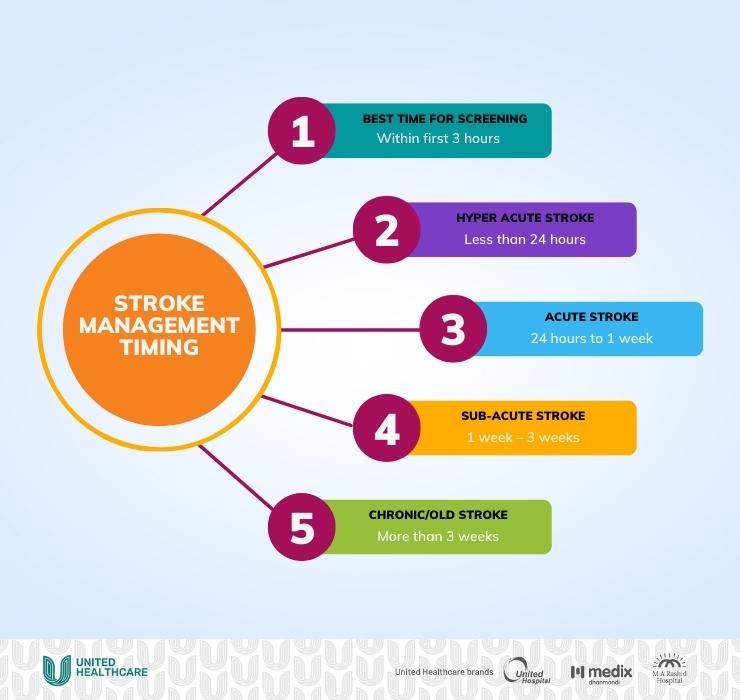
Stroke Management Timing
Best time for Screening : Within first 3 hours
Hyper Acute Stroke : Less than 24 hours
Acute Stroke : 24 hours to 1 week
Sub-acute Stroke : 1 week – 3 weeks
Chronic/Old Stroke : More than 3 weeks
Why Is Stroke So Important?
- Stroke has already reached epidemic proportions.
- Stroke is the leading cause of death and disability worldwide.
- Over 13 million people have stroke each year.
- Around 5.5 million die off stroke each year.
- Globally 1 in 4 adults over the age of 25 will have a stroke in their lifetime.
- Stroke can occur at any age. But risk increases with age
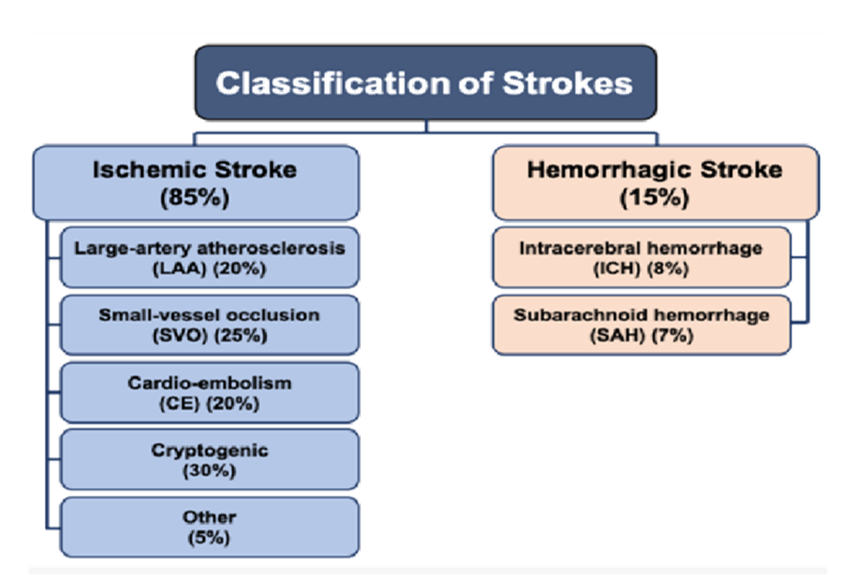
Classification of Strokes:
Symptoms of Stroke
BE FAST Reminder of Stroke Signs:
B - Balance.
Is the person suddenly having trouble with balance or coordination?
E - Eyes.
Is the person experiencing suddenly blurred or double vision or a sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes without pain?
F - Face Drooping.
Is one side of the face drooping? Ask the person to smile.
A- Arm Weakness.
Does one arm drift downward? Have the person raise both arms in the air.
S - Speech Difficulty.
Is he or she slurring their speech or having difficulty getting the words out, right? Have the person repeat a simple phrase.
T - Time to call.
Time to call 10666 and get the person to Uniter Stroke center immediately.
Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Antiplatelets
- Control of blood sugar, blood pressure
- Treatment of complications
- Thrombolysis
- Mechanical Thrombectomy